Python/머신러닝(ML)
Python(31)- 데이터 로더
두설날
2024. 6. 20. 14:47

*이 글을 읽기전에 작성자 개인의견이 있으니, 다른 블로그와 교차로 읽는것을 권장합니다.*
1. 데이터 로더(Data Loader)
- 데이터의 양이 많을 때 배치 단위로 학습하는 방법을 제공

2. 손글씨 인식 모델 만들기
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 런타임 유형 변경 -> GPU 로 변경
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(device)
digits = load_digits()
x_data = digits['data']
y_data = digits['target']
print(x_data.shape)
print(y_data.shape)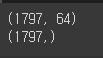
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=5, figsize=(14,8))
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flatten()):
ax.imshow(x_data[i].reshape((8,8)), cmap='gray')
ax.set_title(y_data[i])
ax.axis('off')
x_data = torch.FloatTensor(x_data)
y_data = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
print(x_data.shape)
print(y_data.shape)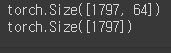
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_data, y_data, test_size=0.2, random_state=2024)
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset=list(zip(x_train, y_train)),
batch_size=64,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=False
)
imgs, labels = next(iter(loader))
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=8, ncols=9, figsize=(14,14))
for ax, img, label in zip(axes.flatten(), imgs, labels):
ax.imshow(img.reshape((8,8)), cmap='gray')
ax.set_title(str(label))
ax.axis('off')
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(64, 10)
)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
epochs = 50
for epoch in range(epochs + 1):
sum_losses = 0
sum_accs = 0
for x_batch, y_batch in loader:
y_pred = model(x_batch)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(y_pred, y_batch)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
sum_losses = sum_losses + loss
y_prob = nn.Softmax(1)(y_pred)
y_pred_index = torch.argmax(y_prob, axis=1)
acc = (y_batch == y_pred_index).float().sum() / len(y_batch) * 100
sum_accs = sum_accs + acc
avg_loss = sum_losses / len(loader)
avg_acc = sum_accs / len(loader)
print(f'Epoch {epoch:4d}/{epochs} Loss: {avg_loss:.6f} Accuracy: {avg_acc:.2f}%')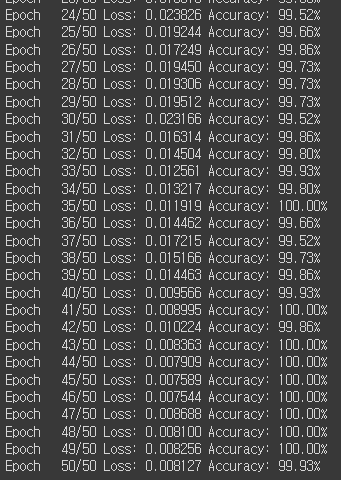
plt.imshow(x_test[10].reshape((8,8)), cmap='gray')
print(y_test[10])
y_pred = model(x_test)
y_pred[10]
y_prob = nn.Softmax(1)(y_pred)
y_prob[10]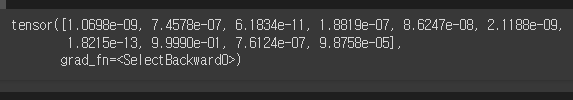
for i in range(10):
print(f'숫자 {i}일 확률: {y_prob[10][i]:.2f}')
# 머신러닝 모델은 정답이 아니라 확률을 내보내기에, 사용자가 직접 확률을 보고 후처리 필요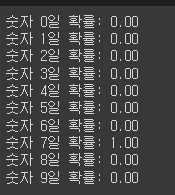
y_pred_index = torch.argmax(y_prob, axis=1)
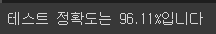
accuracy = (y_test == y_pred_index).float().sum() / len(y_test) * 100
print(f'테스트 정확도는 {accuracy:.2f}%입니다')