
*이 글을 읽기전에 작성자 개인의견이 있으니, 다른 블로그와 교차로 읽는것을 권장합니다.*
1. fstring 객체
conststr1='JavaScript';
const str2 = new String('JavaScript');
str1 == str2; // true
str1 == str2; // false- length() : 문자열의 길이를 반환
- indexof() : 특정 문자나 문자열이 처음으로 등장하는 위치를 인덱스 번호로 반환해주는 프로퍼티 메서드
- charAt() : 특정 문자열에서 전달 받은 인덱스에 위치한 문자를 반환
- includes() : 특정 문자열에서 전달 받은 문자열이 포함되어 있는지 여부를 반환
- substring() : 전달 받은 시작 인덱스부터 종료 인덱스 직전까지의 문자열을 추출, 시작인덱스 default값은 1
- replace() : 원본 문자열의 일부를 전달 받은 문자열로 치환
- split() : 구분자를 기준으로 나눈 후 나뉜 문자열을 하나의 배열에 저장
- trim() : 문자열의 앞 뒤 공백을 제거
- toUpperCase(), toLowerCase() : 문자열을 모두 대, 소문자로 변환
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>string 객체</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const str1 = '안녕하세요. JavaScript';
const str2 = new String('안녕하세요. JavaScript');
console.log(str1==str2);
console.log(str1===str2);
console.log(typeof(str1));
console.log(typeof(str2));
// length: 문자열의 길이를 반환
console.log(str1.length);
// indexof(): 특정 문자나 문자열이 처음으로 등장하는 위치를 인덱스 번호로 반환해주는 프로퍼티 메서드
console.log(str1.indexOf('J'));
console.log(str1.indexOf('Java'));
console.log(str1.indexOf('java')); //못찾아서 -1출력
console.log(str1.indexOf('a'));
console.log(str1.lastIndexOf('J')); //뒤에서부터 찾아줘
// charAt(): 특정 문자열에서 전달 받은 인덱스에 위치한 문자를 반환
console.log(str1.charAt(7));
// includes(): 특정 문자열에서 전달 받은 문자열이 포함되어 있는지 여부를 반환
console.log(str1.includes('Java'));
console.log(str1.includes('java'));
// substring(): 전달 받은 시작 인덱스부터 종료 인덱스 직전까지의 문자열을 추출, 시작인덱스 default값은 1
console.log(str1.substring(7));
console.log(str1.substring(7,11));
// replace(): 원본 문자열의 일부를 전달 받은 문자열로 치환
console.log(str1.replace('안녕하세요', '바뀐 안녕하세요'));
// split(): 구분자를 기준으로 나눈 후 나뉜 문자열을 하나의 배열에 저장
const str3 = '김사과,오렌지,반하나,이메론,배애리,채리'
const students = str3.split(',');
console.log(students);
for(let i in students){
console.log(i, students[i])
}
console.log('------------');
// trim(): 문자열의 앞 뒤 공백을 제거
const str4 = ' JavaScript '
console.log(`😎${str4}`);
console.log(`😎${str4.trim()}공백제거됨`);
// toUpperCase(), toLowerCase(): 문자열을 모두 대, 소문자로 변환
console.log(str1.toUpperCase());
console.log(str1.toLowerCase());
</script>
</body>
</html>
2. Date 객체
날짜, 시간 등을 쉽게 처리할 수 있는 내장 객체입니다.
const 변수명 = new Date(); // 현재 날짜 시간
const 변수명 = new Date(년, 월, 일, 시, 분, 초, 밀리초); // 입력한 날짜 시간에 대한 객체
연도(year)
2자리로 표기
예) 23 -> 1923년
4자리로 표기
예) 2024 -> 2024년
월(month)
0 ~ 11
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Data 객체</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.log(new Date());
console.log(new Date(24,10,11)); //1924.11.11이 잡힘
const current_time = new Date(2024,3,17,9,51,0); //년도는 4글자로 모두 기입, 월(month)는 1달빼서 계산
console.log(current_time);
console.log(`현재 연도: ${current_time.getFullYear()}`);
console.log(`현재 월: ${current_time.getMonth()}`);
console.log(`현재 일: ${current_time.getDate()}`);
console.log(`현재 시간: ${current_time.getHours()}`);
console.log(`현재 분: ${current_time.getMinutes()}`);
console.log(`현재 초: ${current_time.getSeconds()}`);
</script>
</body>
</html>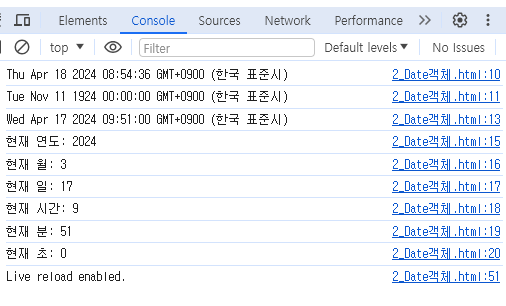
3. 폼(form) 객체
- 일반적인 폼 요소에 접근할 때 사용합니다.
- document.forms 컬렉션을 이용해서도 접근이 가능합니다.
<form name=''myform id='regform' method='post' action='/regist'>
아이디: <input type='text' name='userid' id='userid'><br>
비밀번호: <input type='password' name='userpw' id='userpw><br>
</form>
폼 접근하기
const frm = document.myform; // name
const frm = document.forms['myform']; // name
const frm = document.forms[0]; // 폼 중에서 첫번째 폼
const frm = document.getElementById('regform'); // id
아이디 입력상자에 접근하기
window 객체
웹 브라우저의 창이나 탭을 설정하기 위한 객체들이며, 웹 브라우저는 window 객체를 이용하여 브라우저 창을 표현할 수 있습니다. 모든 내장객체의 최상위 객체입니다.
window.alert()
window.confirm()
window.prompt()
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>폼 객체</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>폼 객체</h2>
<form action="/regist" name="frm1" id="frm1">
<input type="text" name="userid" id="userid" placeholder="아이디를 입력하세요"><br>
<input type="password" name="userpw" id="userpw" placeholder="비밀번호를 입력하세요">
</form>
<form action="/searcg" name="frm2" id="frm2">
<input type="search" name="search" id="search" placeholder="검색어를 입력하세요"> <button type="button" onclick="sendit()">확인</button>
</form>
<script>
const frm1 = document.frm1;
console.log(frm1);
console.log(frm1.userid.placeholder);
document.getElementById('userid').value = 'apple';
document.forms['frm1'].elements['userpw'].value='1004';
document.forms['frm2'].elements['search'].value='코리아IT아카데미';
const frm2 =document.frm2;
console.log(frm2.search.placeholder)
// frm2의 search에 있는 placeholder를 콘솔에 출력
// frm2의 search를 forms 컬렉션의 인덱스로 찾아 search 요소에 '코리아IT아카데미'를 입력
function sendit(){
alert('확인을 눌렀어요!');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
setTimeout()
일정 시간이 지난 후 매개변수로 제공된 함수를 실행, 함수는 콜백형태로 들어갑니다.
const 변수명 = function(){
...
}
const st = setTimeout(변수명, 밀리초);
clearTimeout()
일정 시간 후에 일어날 setTiemout()을 취소합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>setTimeout</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const hello = function(){
alert('안녕하세요, JavaScript');
}
const st = setTimeout(hello, 5000); // 5초
clearTimeout(st);
</script>
</body>
</html>4. setInterval()
일정 시간마다 매개변수로 제공된 함수를 실행합니다.
clearInterval()
일정 시간마다 일어날 setInterval()을 취소합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>setInterval</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const hello = function(){
console.log('안녕하세요, JavaScript');
}
const si = setInterval(hello, 3000);
const clearInter = function(){
clearInterval(si);
console.log('hello()가 중지되었습니다');
}
</script>
<p><button onclick="clearInter()">중지</button></p>
</body>
</html>
문제.
현재 시간을 출력하는 문서를 만듭니다.
(단, 시작 버튼을 누르면 콘솔에 현재 시간을 초마다 출력하고, 중지 버튼을 누르면 시간이 정지됨. 다시 시작 버튼을 누르면 시간이 다시 출력되기 시작)
[시작] [중지]
콘솔
2024-04-17 11:16:00
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>시간출력</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>시간출력</h2>
<script>
// 출력형태 설정
const print = function(){
const date = new Date()
console.log(`
${date.getFullYear()}-${date.getMonth()+1}-${date.getDate()} ${date.getHours()}:${date.getMinutes()}:${date.getSeconds()}
`);
}
//시작버튼
const start = function(){
console.log('출력 시작');
start1 = setInterval(print,1000);
}
//중지버튼
const clearInter =function(){
clearInterval(start1);
console.log('출력 중지');
}
</script>
<p>
<button onclick="start()">시작</button>
<button onclick="clearInter()">중지</button>
</p>
</body>
</html>
5. location 객체
현재 브라우저에 표시된 HTML 문서의 주소를 얻거나, 브라우저에 새 문서를 불러올 때 사용합니다.
https://koreaisacademy.com/community/tv_view.asp?idxnum=198&clkMater=&txtMenu=&txtCurPage=1&selMater=&gubun=1
URL
https://koreaisacademy.com/community/tv_view.asp
protocol: 콜론을 포함하는 http, https, ftp 등 프로토콜 정보를 반환
hostname: 호스트의 이름과 포트번호를 반환
예) https://
hostname: 호스트의 이름과 포트번호를 반환
예) https://koreaisacdemy.com/
pathname: URL 경로부분을 반환
예) /community/tv_view.asp
href: 페이지 URL 전체 정보를 반환 또는 URL을 지정하여 페이지를 이동시킵니다.
reload(): 새로고침
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>location 객체</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>location 객체</h2>
<script>
function pageInfo(){
console.log(`현재 문서의 URL주소: ${location.href}`);
console.log(`현재 문서의 protocol: ${location.protocol}`);
console.log(`현재 문서의 hostname: ${location.hostname}`);
console.log(`현재 문서의 pathname: ${location.pathname}`);
}
function sendit(){
location.href = 'https://python.org'
}
</script>
<p>
<button onclick="pageInfo()">페이지 정보</button>
<button onclick="sendit()">이동하기</button>
<button onclick="location.reload()">새로고침</button>
</p> // location.reload()는 본래 있는 함수, 기능
</body>
</html>

6. history 객체
- 브라우저의 히스토리 정보를 문서와 문서상태 목록으로 저장하는 객체입니다.
- 사용자의 개인 정보를 보호하기 위해 이 객체의 대부분의 기능을 제한합니다.
back(): 페이지를 뒤로 이동시킴
forward(): 페이지를 앞으로 이동시킴
go(0): 새로고침, location.reload()와 같은 기능
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>history 객체</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>history 객체</h2>
<button onclick="history.back()">뒤로</button>
<button onclick="history.forward()">앞으로</button>
<button onclick="history.go(0)">새로고침</button>
</body>
</html>7. navigator 객체
브라우저 공급자 및 버전 정보 등을 포함한 브라우저에 대한 정보를 저장하는 객체입니다.
geolocation: GPS정보를 수신하는 프로퍼티
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>navigator</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>navigator</h2>
<script>
const success = function(loc){
console.log(loc.coords.latitude);
console.log(loc.coords.longitude);
}
const fail = function(msg){
console.log(msg.code);
}
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(success, fail)
</script>
</body>
</html>
8. Document 객체
- DOM(Document Object Model)
- HTML문서 또는 XML문서 등을 접근하기 위한 일종의 인터페이스 역할입니다.
- 문서내의 모든 요소를 정의하고 각각의 요소에 접근하는 방법을 제공합니다.
- 웹 페이지 자체(body)를 의미하는 객체입니다.
- 웹 페이지에 존재하는 HTML 요소에 접근하고자 할 때 반드시 document객체로부터 시작합니다.
getElementById() : 해당 아이디의 요소를 선택
getElementsByTagName() : 해당 태그 이름의 요소를 모두 선택
getElementsByClassName() : 해당 클래스에 속한 요소를 모두 선택
getElementsByName() : 해당 name 속성값을 가지는 요소를 모두 선택
querySelectorAll() : 선택자로 선택되는 요소를 모두 선택
querySelector() : 선택자로 선택되는 요소를 선택
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>문서 객체 모델1</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>문서 객체 모델1</h2>
<ul>
<li name="markup">HTML</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li id="javascript" class="js">JavaScript</li>
<li class="js">React</li>
<li class="backend">Apache</li>
<li class="backend">NgineX</li>
<li id="nodejs" class="js">Node.js</li>
<li id="vue" class="js">Vue</li>
</ul>
<script>
const tagName = document.getElementsByTagName('li');
for(let i=0; i<tagName.length;i++){
console.log(tagName[i]);
tagName[i].style.color = 'gold'
}
console.log('-------------');
const className = document.getElementsByClassName('js');
for(let i=0; i<className.length; i++){
console.log(className[i]);
className[i].style.color = 'deeppink'
}
console.log('-------------');
const id = document.getElementById('javascript');
console.log(id);
id.style.color = 'greenyellow';
const name = document.getElementsByName('markup');
for(let i=0; i<name.length; i++){
console.log(name[i]);
name[i].style.color = 'blue'
}
console.log('-------------');
const qsa = document.querySelectorAll('li.backend');
for(let i=0; i<qsa.length; i++){
console.log(qsa[i]);
qsa[i].style.color = 'green'
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>문서 객체 모델2</title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
const gnb = document.getElementById('gnb');
console.log(gnb);
console.log(gnb.parentNode);
console.log(gnb.children[0]);
console.log(gnb.children[1]);
console.log(gnb.children[0].children[0]);
console.log(gnb.children[0].children[1]);
console.log(gnb.children[0].children[0].nextElementSibling);
console.log(gnb.children[0].firstChild);
console.log(gnb.children[0].firstElementChild);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>문서 객체 모델2</h2>
<div>
<nav id="gnb">
<ul>
<li>내용 1</li>
<li>내용 2</li>
<li>내용 3</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
</body>
</html>9. 노드(node)
HTML DOM은 노드라고 불리는 계층적 단위에 정보를 저장합니다.
노드 종류
문서 노드: 문서 전체를 나타내는 노드
요소 노드: HTML 모든 요소는 요소노드이며, 속성노드를 가질 수 있습니다.
속성 노드: HTML 모든 요소는 속성노드이며, 속성노드에 관한 정보를 가지고 있습니다.
텍스트 노드: HTML 모든 텍스트는 텍스트노드
주석 노드: HTML 모든 주석은 주석노드
노드의 관계
parentNode: 부모 노드
children: 자식 노드
childNodes: 자식 노드 리스트
firstChild: 첫번째 자식 노드
firstElementChild: 첫번째 자식 요소 노드
lastChild: 마지막 자식 노드
nextSibling: 다음 형제 노드
previousSibling: 이전 형제 노드
DOM 노드: HTML 문서의 각 태그, 텍스트, 속성 등을 나타내는 객체입니다.
DOM 노드는 요소 노드, 텍스트 노드, 속성 노드 등으로 분류됩니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Document Object Model</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Title</h1>
<p>Hello, World!</p>
</body>
</html>위 HTML 문서의 DOM 트리는 다음과 같습니다:
Document
└── html
├── head
│ └── title
│ └── "Document Object Model"
└── body
├── h1
│ └── "Title"
└── p
└── "Hello, World!"// <h1> 요소에 접근하기
let heading = document.querySelector('h1');
console.log(heading.textContent); // "Title"// <p> 요소의 텍스트 변경하기
let paragraph = document.querySelector('p');
paragraph.textContent = "Hello, DOM!";// <h1> 요소에 id 속성 추가하기
heading.setAttribute('id', 'main-title');
console.log(heading.getAttribute('id')); // "main-title"// 새로운 <p> 요소를 생성하고 <body>에 추가하기
let newParagraph = document.createElement('p');
newParagraph.textContent = "New Paragraph";
document.body.appendChild(newParagraph);// 기존 <p> 요소 삭제하기
paragraph.remove();
- appendChild() : 새로운 노드를 해당 노드의 자식 노드 리스트 맨 마지막에 추가
- insertBefore() : 새로운 노드를 특정 자식 노드 바로 옆에 추가
- createElement() : 새로운 요소 노드를 만듦
- innerHTML : HTML요소와 텍스트를 삽입
- innerText : 텍스트만 삽입
- createAttribute() : 새로운 속성 노드를 만듦
- createTextNode() : 새로운 텍스트 노드를 만듦
- removeChild() : 자식 노드 리스트에서 특정 자식 노드를 제거, 노드가 제거됨면 해당 노드를 반환, 노드가 제거될 때 노드의 자식들도 다같이 제거
- removeAttribute() : 특정 속성 노드를 제거
- cloneNode() : 기존의 존재하는 노드와 동일한 새로운 노드를 생성하여 반환(true 자식까지 복사, false 자식은 복사하지 않음)
- setAttribute()
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>노드 메서드</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>노드 메서드</h2>
<script>
function appendNode(){
const parent = document.getElementById('list');
console.log(parent);
const newItem = document.getElementById('item1');
console.log(newItem);
// appendChild(): 새로운 노드를 해당 노드의 자식 노드 리스트 맨 마지막에 추가
parent.appendChild(newItem);
}
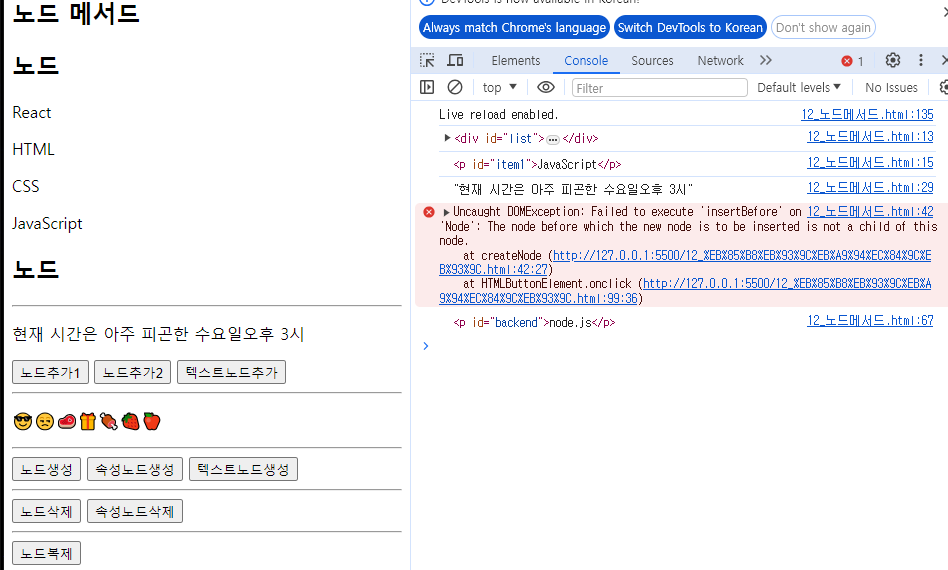
function insertNode(){
const parent = document.getElementById('list');
const backend = document.getElementById('backend');
const newItem = document.getElementById('item2');
// insertBefore(): 새로운 노드를 특정 자식 노드 바로 옆에 추가
parent.insertBefore(newItem, backend);
}
function appendText(){
const text = document.getElementById('text').firstChild;
console.log(text);
// 새로운 노드를 텍스트 데이터로 추가
text.insertData(7, '아주 피곤한 수요일');
}
function createNode(){
const newItem = document.getElementById('item1');
// createElement(): 새로운 요소 노드를 만듦
const newNode = document.createElement('p'); //<p></p>
// <p><strong>😎 새로운 요소가 추가됨</strong></p>
// innerHTML: HTML요소와 텍스트를 삽입
// innerText: 텍스트만 삽입
newNode.innerHTML = '<strong>😎 새로운 요소가 추가됨</strong>'
document.body.insertBefore(newNode, newItem);
}
function createAttr(){
const newItem = document.getElementById('item2');
// createAttribute(): 새로운 속성 노드를 만듦
const newAttr = document.createAttribute('style'); // style=''
// style='color:deeppink; background-color:gold'
newAttr.value = 'color:deeppink; background-color:gold';
// <p id='item2' style='color: deeppink; background-color:gold;'>React</p>
newItem.setAttributeNode(newAttr);
}
function createText(){
const textNode = document.getElementById('ct');
// createTextNode(): 새로운 텍스트 노드를 만듦
const newText = document.createTextNode('😎😒🥩🎁🍖🍓🍎');
textNode.appendChild(newText);
}
function removeNode(){
const parent = document.getElementById('list');
const removeItem = document.getElementById('backend');
// removeChild(): 자식 노드 리스트에서 특정 자식 노드를 제거, 노드가 제거됨면 해당 노드를 반환, 노드가 제거될 때 노드의 자식들도 다같이 제거
const result = parent.removeChild(removeItem);
console.log(result);
}
function removeAttr(){
const newItem = document.getElementById('item2');
// removeAttribute(): 특정 속성 노드를 제거
newItem.removeAttribute('style');
}
function cloneElement(){
const parent = document.getElementById('list');
const originItem = document.getElementById('cl');
// cloneNode(): 기존의 존재하는 노드와 동일한 새로운 노드를 생성하여 반환(true 자식까지 복사, false 자식은 복사하지 않음)
parent.appendChild(originItem.cloneNode(true));
}
</script>
<h2 id="cl">노드</h2>
<div id="list">
<p id="backend">node.js</p>
<p>HTML</p>
<p>CSS</p>
</div>
<p id="item2">React</p>
<p id="item1">JavaScript</p>
<hr>
<p id="text">현재 시간은 오후 3시</p>
<button onclick="appendNode()">노드추가1</button>
<button onclick="insertNode()">노드추가2</button>
<button onclick="appendText()">텍스트노드추가</button>
<hr>
<p id="ct"></p>
<hr>
<button onclick="createNode()">노드생성</button>
<button onclick="createAttr()">속성노드생성</button>
<button onclick="createText()">텍스트노드생성</button>
<hr>
<button onclick="removeNode()">노드삭제</button>
<button onclick="removeAttr()">속성노드삭제</button>
<hr>
<button onclick="cloneElement()">노드복제</button>
</body>
</html>cloneNode(): 기존의 존재하는 노드와 동일한 새로운 노드를 생성하여 반환(true 자식까지 복사, false 자식은 복사하지 않음)
'JavaScript > Vanila JS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JavaScript 기초(6)-정규 표현식, 이벤트 핸들러 (0) | 2024.04.18 |
|---|---|
| JavaScript 기초(4)- 함수, 객체, 프로토타입 (0) | 2024.04.16 |
| JavaScript 기초(3)- forEach반복문+기타 반복문 (0) | 2024.04.16 |
| JavaScript 기초(2)- 제어문 If, Switch (0) | 2024.04.15 |
| JavaScript 기초(1)- 상수, 데이터 타입, 형 변환 (0) | 2024.04.15 |



